How ‘Mind Rooms’ Offers a Unique Approach to Mental Health
A New Perspective on Mental Health Challenges
Mental health challenges like rumination, intrusive thoughts, and obsessive-compulsive behaviors are notoriously difficult to tackle. Traditional methods often fall short in addressing the root causes of these issues, leading to temporary relief rather than lasting solutions. The self-help book “Mind Rooms” by Johannes Faupel introduces a revolutionary approach that not only acknowledges the complex neural mechanisms behind these conditions but offers a practical way to address them.
The Core Concept of ‘Mind Rooms’: Mental Spaces for Cognitive Freedom
The unique approach of “Mind Rooms” is rooted in the idea of creating mental spaces—or ‘rooms’—where intrusive thoughts can be organized, stored, and revisited on your own terms. This technique draws on the principles of cognitive psychology and modern neuroscience to transform how we interact with our thoughts.
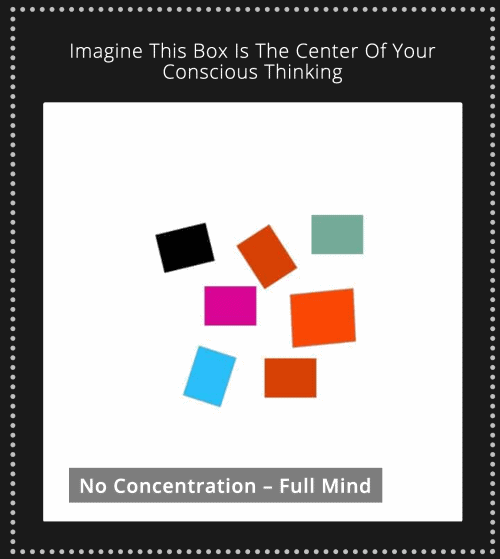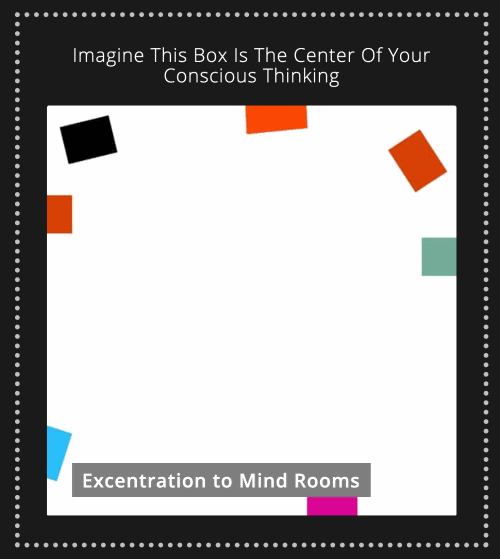
By visualizing specific thoughts as items that can be placed into a designated mental room, individuals gain psychological distance from these thoughts. This process is called **excentration**—a term that represents mentally placing disruptive or persistent thoughts into a compartmentalized ‘space’ within the mind. This allows individuals to temporarily set aside intrusive thoughts without needing to suppress or deny them. The benefit is a reduction in cognitive load, which subsequently improves mental clarity and emotional resilience.
Engaging System 1 Thinking and System 2 Thinking
The technique presented in “Mind Rooms” uniquely integrates the dual-process theory of the mind, originally conceptualized by Nobel Prize-winning psychologist Daniel Kahneman as **System 1** and **System 2** thinking.
– System 1 Thinking: This is fast, automatic, and often emotional. It’s the system that drives our immediate responses and underpins many of our instinctive reactions to triggers—like intrusive thoughts. “Mind Rooms” helps calm the hyperactivity of System 1 by providing an immediate action that addresses the perceived cognitive threat: mentally relocating the thought.
– System 2 Thinking: This is the slower, more deliberate mode of thinking that requires conscious effort. It’s responsible for rational analysis and thoughtful decision-making. By revisiting thoughts placed in ‘Mind Rooms’ during moments of calm, individuals engage System 2, allowing for rational reflection and problem-solving. This conscious revisit helps address the content of these thoughts with clarity and logic, breaking the cycle of rumination.
Addressing the Default Mode Network (DMN) and Salience Network
Modern neuroscience has identified two primary neural networks involved in rumination and obsessive thinking: the default mode network (DMN) and the salience network. The default mode network, associated with self-referential thinking and mind-wandering, becomes hyperactive during rumination, causing individuals to fixate on negative emotions and thoughts.
“Mind Rooms” intervenes in this process by redirecting the brain’s focus. When an intrusive thought is placed into a ‘mental room,’ it shifts the activation away from the default mode network, thereby reducing its hyperactivity. This helps in decreasing the repetitive, self-referential loops that often lead to anxiety and depression.
Similarly, the salience network, which prioritizes emotional stimuli, can misfire in individuals prone to rumination or OCD, giving undue importance to intrusive thoughts. By categorizing these thoughts as something that can be safely set aside in a ‘room,’ the salience network is recalibrated to no longer treat these thoughts as immediate threats requiring attention.
What are the Practical Benefits of ‘Mind Rooms’?
- Reduced Cognitive Load: By placing intrusive thoughts in a mental room, cognitive resources are freed up, making it easier to focus on tasks and responsibilities without constant mental interruption.
- Emotional Regulation: The act of mentally storing a thought helps decrease the immediate emotional response, leading to a calmer state of mind. It offers a proactive way to deal with emotional triggers without succumbing to emotional overwhelm.
- Structured Reflection: By revisiting thoughts in a more controlled manner, individuals can engage in structured reflection rather than being overwhelmed by emotional intensity. This allows for a healthier form of introspection that promotes personal growth.
How ‘Mind Rooms’ Stands Out from Traditional Techniques
Traditional techniques like mindfulness, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and positive affirmations have their merits, but they often fail to address the neurological basis of intrusive thoughts and rumination. Mindfulness asks individuals to observe their thoughts without judgment, which can be difficult when those thoughts are distressing. CBT attempts to restructure thought patterns but requires active engagement that may not always be feasible in emotionally heightened states.
“Mind Rooms” offers an innovative alternative by neither forcing direct confrontation nor ignoring the thoughts. Instead, it provides a balanced way to acknowledge and categorize these thoughts. This structured yet non-confrontational approach is particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle with high anxiety or obsessive tendencies, as it respects the brain’s natural defense mechanisms while gently redirecting them.
Conclusion: A Neuroscience-Backed Approach to Mental Wellness
“Mind Rooms” presents a unique and effective strategy for overcoming rumination, intrusive thoughts, and obsessive tendencies by utilizing a combination of cognitive psychology, visualization techniques, and modern neuroscience. By addressing the neurological basis of these issues—namely the dysfunction in the default mode network and salience network —this approach offers not just temporary relief but the potential for lasting change.
The benefits of “Mind Rooms” lie in its simplicity: by organizing thoughts into mental spaces, it provides immediate relief from cognitive overload and sets the stage for rational, deliberate processing later. This makes it an invaluable tool for those seeking a practical, science-backed method for improving their mental health and achieving lasting emotional balance.